What is Radon?
Radon is a cancer-causing natural radioactive gas that you can't see, smell or taste. If found in the home, it can pose a danger to your family's health. Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, and is the second leading cause of lung cancer in America. Your home should be tested for Radon, and you should consider radon mitigation (also known as radon remediation or radon gas abatement) if radon levels are between 2 and 4 pCi/L. A normal modern house will trap Radon because we want our house to minimize the leakage of air to the outside or infiltration of air to the inside. This thermal separation and insulation process makes our houses trap gasses longer, resulting in higher concentration of any poisonous gas released in our homes, including Radon.
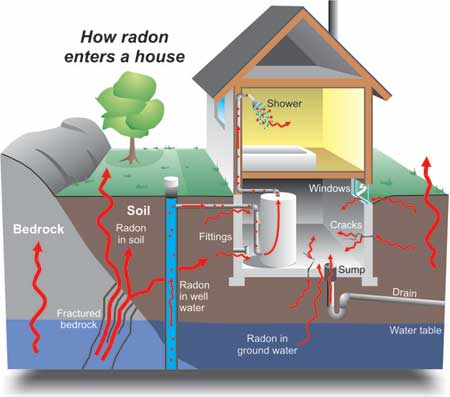
How Does Radon Enter My Home?
Radon is a radioactive gas produced from the natural decay of uranium, which is found in nearly all rocks and soils. This gas moves through the ground and enters your home through:
- • Cracks in the basement floor
• Slab joints
• Floor drains
• Cracks and cavities in the walls
• Sump pumps
• Loose fitting pipes
Radon enters your home primarily because of the difference between the inside and outside air pressure. Air pressure inside your home is usually lower than pressure in the soil around your homes foundation. Because of this difference in pressure, your home acts like a vacuum, drawing Radon in through cracks in the foundation and other openings. The amount of Radon that accumulates depends on the amount of Radon being released by materials below the building, the kind of construction materials and ventilation systems used in the building, as well as the temperature. For example, a heated building in a cold climate may draw in more Radon than a building in a warm climate. Since most Radon enters the air from soil or rock, the lower rooms in a building are usually more at risk than the rooms higher up. It is also possible for one home to be exposed to high levels of Radon while the home directly next door is not.
